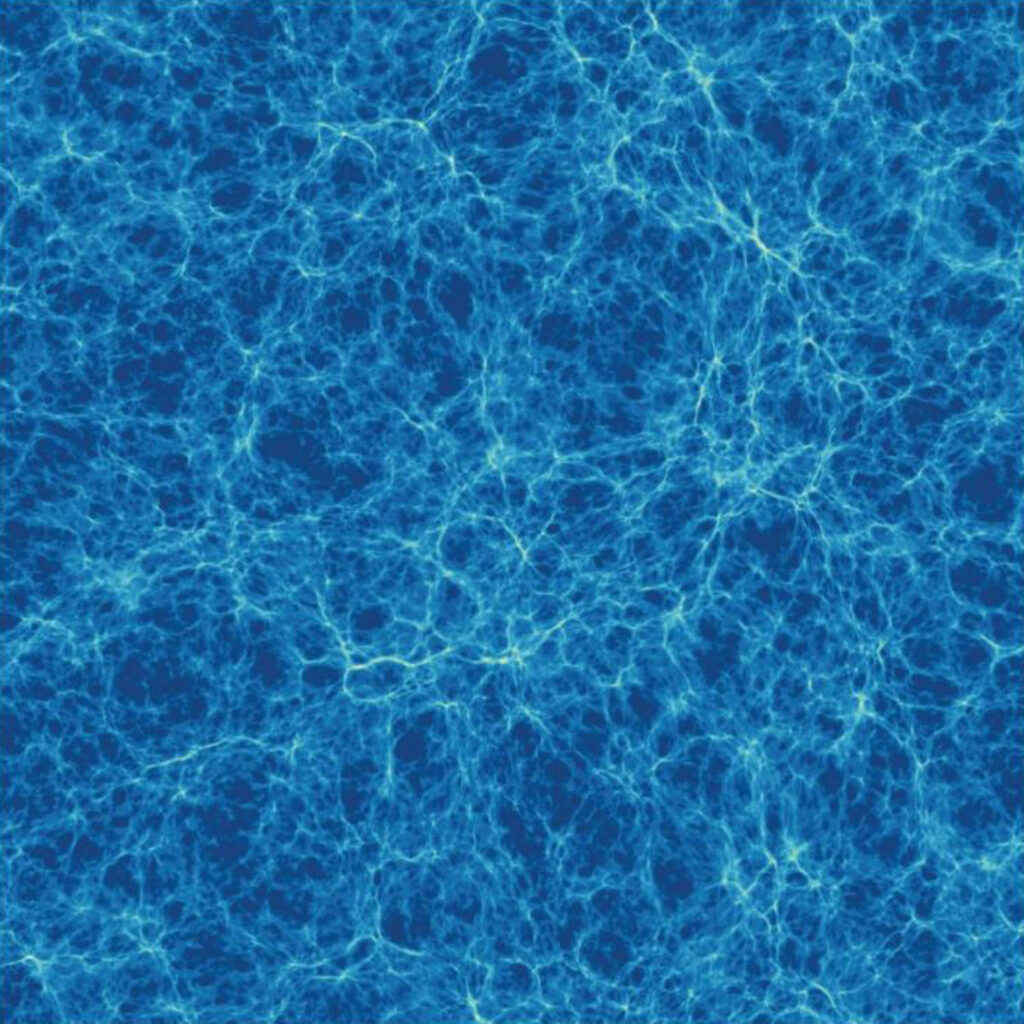
Cosmic filaments are massive thread-like formations, comprising huge amounts of matter, including galaxies, gas and dark matter.
They can be 500 million light-years long but just 20 million light-years wide.
At their largest scale, they divide the Universe into a vast gravitationally linked lattice interspersed with enormous dark matter voids.
“The spine of cosmic filaments is pretty much the highway of galactic migration, with many galaxies encountering and merging along the way,” said Dr. Charlotte Welker, a researcher at McMaster University, the ARC Centre of Excellence for Astrophysics in 3 Dimensions (ASTRO 3D) and ICRAR.
Using data gathered by the Sydney-AAO Multi-object Integral-field spectrograph (SAMI) at the Anglo-Australian Telescope, Dr. Welker and colleagues studied each of the target galaxies and measured its spin in relation to its nearest filament.