Locomotor energetics are an important determinant of an animal’s ecological niche. It is commonly assumed that animals minimize locomotor energy expenditure by selecting gait kinematics tuned to the natural frequencies of relevant body parts. We demonstrate that this allows estimation of the preferred step frequency and walking speed of Tyrannosaurus rex, using an approach we introduce as the Natural Frequency Method.
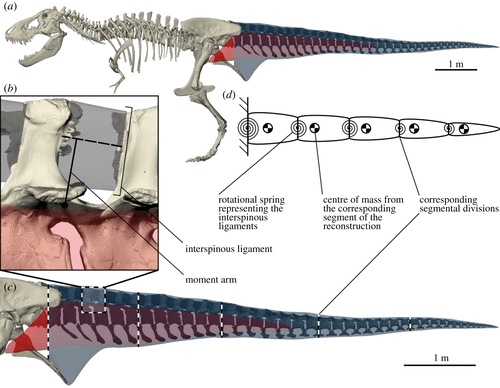
Although the tail of bipedal dinosaurs was actively involved in walking, it was suspended passively by the caudal interspinous ligaments. These allowed for elastic energy storage, thereby reducing the metabolic cost of transport. In order for elastic energy storage to be high, step and natural frequencies would have to be matched. Using a 3D morphological reconstruction and a spring-suspended biomechanical model, we determined the tail natural frequency of T. rex (0.66 s−1, range 0.41–0.84), and the corresponding walking speed (1.28 m s−1, range 0.80–1.64), which we argue to be a good indicator of preferred walking speed (PWS).
The walking speeds found here are lower than earlier estimations for large theropods, but agree quite closely with PWS of a diverse group of extant animals. The results are most sensitive to uncertainties regarding ligament moment arms, vertebral kinematics and ligament composition. However, our model formulation and method for estimation of walking speed are unaffected by assumptions regarding muscularity, and therefore offer an independent line of evidence within the field of dinosaur locomotion.